dpkg安装Nginx
Debian使用apt-get作为软件包管理器,所以我们可以使用apt-get直接安装dpkg,进而安装Nginx:
apt-get install nginx安装完以后,输入whereis nginx查看Nginx的安装位置,其中的nginx.conf为Nginx的配置文件。
常用Nginx命令
这边给大家介绍一些Nginx常用命令:
|
命令 |
命令含义 |
|---|---|
|
nginx |
打开 nginx |
|
nginx -t |
测试配置文件是否有语法错误 |
|
nginx -s reopen |
重启Nginx |
|
nginx -s reload |
重新加载Nginx配置文件 |
|
nginx -s stop |
强制停止Nginx服务 |
|
nginx -s quit |
安全地停止Nginx服务(即处理完所有请求后再停止服务) |
1. 我想让一个demo 站点直接域名访问,不带端口,所以想用 80 端口启动对应前端工程。
发现 80 被 nginx 占用:
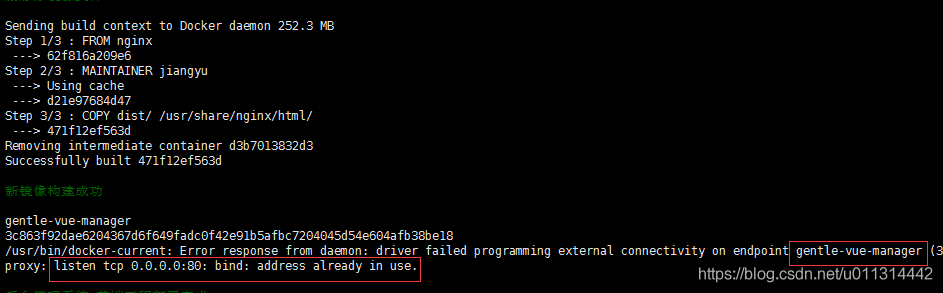
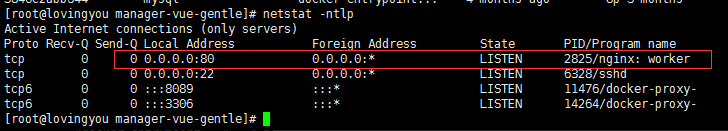
2. 修改 nginx 端口,只需要修改其监听的端口就行了。
找到 nginx 的配置文件,并编辑 listen 后面的端口号就行了。
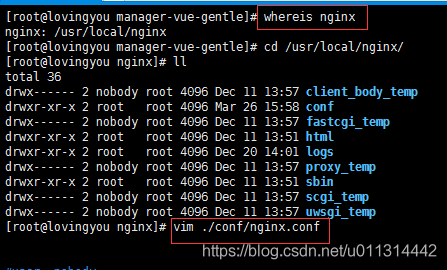
如 我把原本的 80 改为了8082:
文件目录:
root@li:/etc/nginx/sites-available#
dir
default(*用vi default修改这个文件)
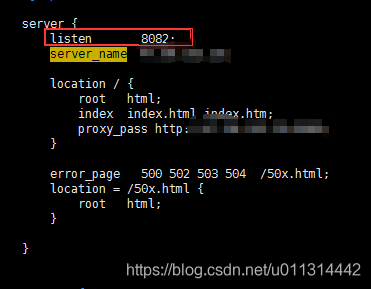
3. 重新加载 nginx 配置、重启 nginx 都行。
# 启动
./nginx
./nginx -s stop
./nginx -s quit
./nginx -s reload再次查看,nginx 的端口已经变更为 8082 了。
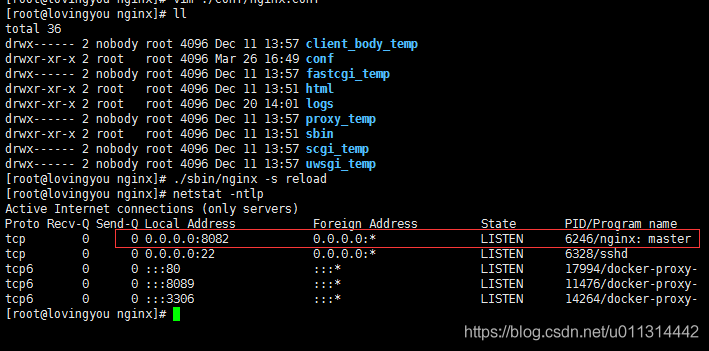
4. 重新启动原前端工程成功。

cd /var/www/html;
##
# You should look at the following URL’s in order to grasp a solid understanding
# of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx.
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/
# https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/
# https://wiki.debian.org/Nginx/DirectoryStructure
#
# In most cases, administrators will remove this file from sites-enabled/ and
# leave it as reference inside of sites-available where it will continue to be
# updated by the nginx packaging team.
#
# This file will automatically load configuration files provided by other
# applications, such as Drupal or WordPress. These applications will be made
# available underneath a path with that package name, such as /drupal8.
#
# Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples.
##
# Default server configuration
#
server {
listen 16601 default_server;
listen [::]:16601 default_server;
# SSL configuration
#
# listen 443 ssl default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl default_server;
#
# Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332
#
# Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782
#
# Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package
# Don’t use them in a production server!
#
# include snippets/snakeoil.conf;
root /var/www/html;
# Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location / {
# First attempt to serve request as file, then
# as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404.
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
# pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets):
# fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
# # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets):
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache’s document root
# concurs with nginx’s one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# Virtual Host configuration for example.com
#
# You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that
# to sites-enabled/ to enable it.
#
#server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80;
#
# server_name example.com;
#
# root /var/www/example.com;
# index index.html;
#
# location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# }
#}